ESG Mapper: Doing Well by Doing Good Consistently
Mission Statement
Our mission is to develop a user-friendly tool that filters out and labels the Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) statements from any PDF documents according to the Sustainability and Accounting Standards Board (SASB) materiality framework. In order to do so, we fine-tuned BERT models into a text filter to identify ESG-relevant texts, followed by SASB classifications at two levels (parent and child labels). The users will enjoy our tool directly on a web-based user interface (UI) that allows users to upload any PDF inputs, read a summary of SASB topics from the text, and view the distribution of SASB-labeled texts.
The Problem
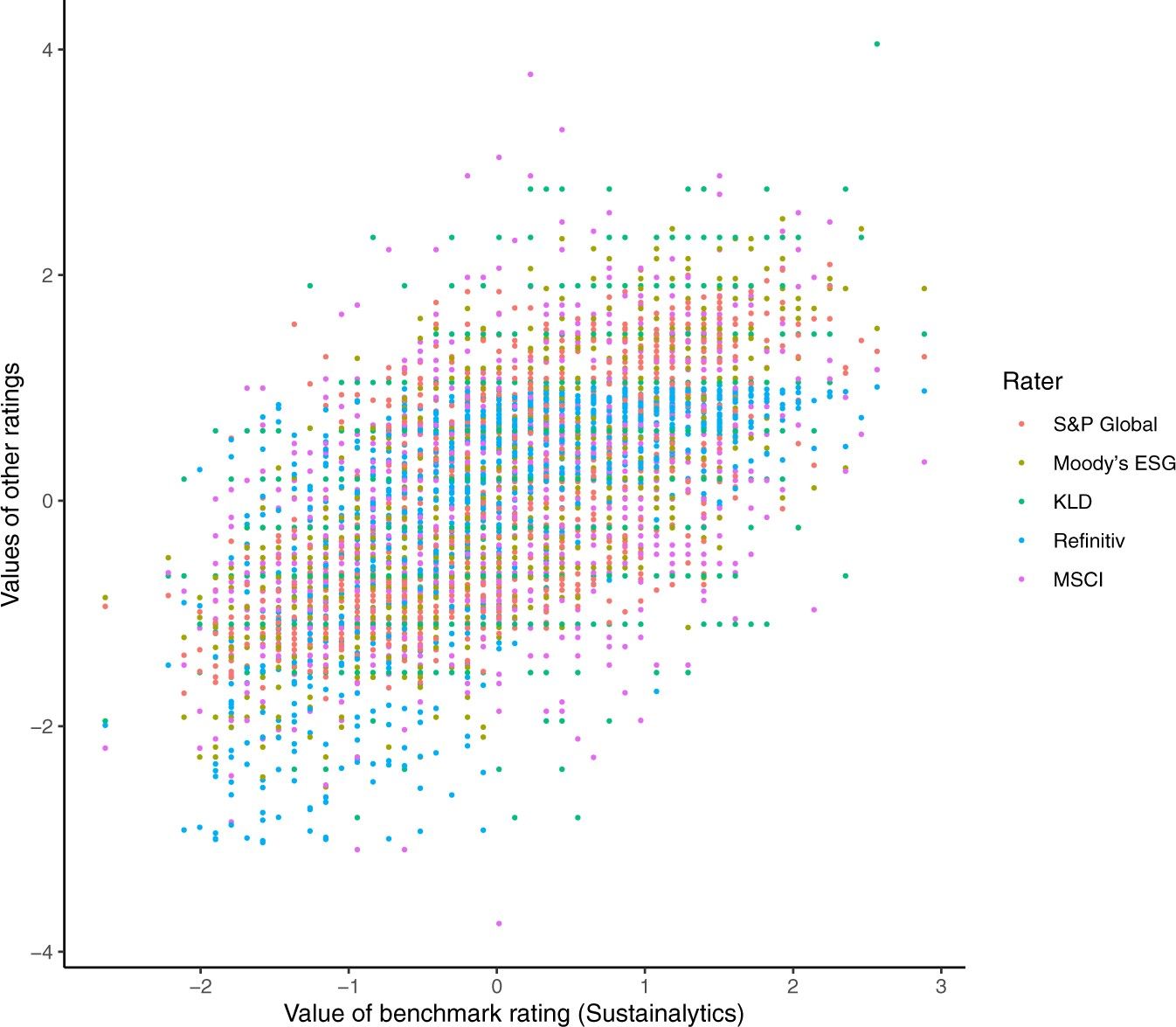
Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) is a set of aspects, considered when investing in companies, that recommends taking environmental issues, social issues, and corporate governance issues into account. While there is a rising network of ESG ratings, they are inconsistent across reporting standards, rating agencies, and governance bodies. Recently, after examining six well-known ESG ratings, The Aggregation Confusion Project at MIT found that the scores of these ratings on the same companies often diverged. The major contributor to this problem is the Jingle-Jangle Fallacy, a term often used in information science (e.g., Larsen & Bong, 2016; Song et al., 2021) to describe the inconsistent use of terminologies and measurements across domains of information and knowledge. Specifically, the definitions and measures adopted by different ratings differ significantly and how they relate to each other remains quite unclear.
The Jingle-Jangle Fallacy in the ESG rating industry is problematic for a few reasons.
First, it makes it difficult if not impossible to compare ratings across standards. As a consequence, it leaves companies much leeway for questionable practices to selectively report some measures from a rating in favor of their position and hide others where firms may be at a disadvantage. Second, it makes it costly for analysts to compare and synthesize the findings about the impact of ESG dimensions, from trade-offs among stakeholder interests to long-term economic value.
As a solution, we created a Large Language Model (LLM)-based end-to-end platform that takes PDF documents uploaded by users, classifies texts into ESG topics following the SASB standard, and reports the frequency and distribution of sentences by each SASB label.
Motivation and Market Opportunity
The Global ESG investment space is seeing fractures appearing due to concerns about inconsistent ratings. The global ESG market is estimated to hit $50 trillion in 2025 (McCabe, 2023). However, ESG score providers, who are following inconsistent approaches, are drawing criticism because unreliable ESG ratings can lead to greenwashing.
The project aims to use a systematic natural language processing (NLP) approach to standardize the ESG categorization process which subsequently drives ESG ratings. A standardized and consistent ESG rating system serves as a transparent means for investors, customers, NGOs, and the public to make well-informed decisions based on ESG considerations. It will also help improve the reliability and integrity of the ESG investment market space and attract capital towards companies that focus on society, the environment, and a sustainable future for all stakeholders.
Our target users are anyone who needs an efficient approach to comparing companies against a standard framework of ESG topics, such as ESG investment analysts and ESG regulators/auditors.
The direct impact of our tool is to replace labor costs for ESG labeling and comparison, which is estimated to count for roughly $170 million per year for a large ESG rating agency.
Key Features
INTERACTIVE
ESG mapper is a user-friendly, web based tool that takes a single input of any PDF document uploaded by the user
REAL-TIME RESULT
Compehensive results are generated in real time. It takes roughly 3-5 minutes for ESG mapper to finish summarization, prediction and present results after user input
END-TO-END WORKFLOW
ESG mapper kicks off when a user drags and drops a PDF document, and the rest happens automatically in the backgorund.
DETAIL-ORIENTED
Results generated by ESG mapper are comprehensive and detail oriented. They can be as high level as a sandkey diagram to help users view the distribution of ESG label distribution at a glance, and well as being specific enough to include confidence intervals of predictions to help investment professionals make informed decisions.
CONSISTENCY, AUTOMATION AND ACCURACY
In a highly regulated market as the Financial Market, rules and standards are the heart and soul of responsible investing. We aim standardize ESG rating so that ESG driven investment decisions are transparent, standardized and regulation-compliant.
Data Source and Data Science Approach
Our training data were collected from the SASB portal. Documents were sourced from SASB because it offers the most comprehensive interpretation of ESG terminology, and it is the most influential standard across industries. We scraped the SASB reports portal to generate a list of documents that we will use for our training data. For the consistency of the language, we limited our data to US firms only, including SASB Reports and Disclosures. In total, we downloaded 37 such documents, each of which contains 10-20 pages of text.
Below is the SASB label taxonomy, including five parent-level labels and 26 child-level labels.
How It Works

Model Evaluation
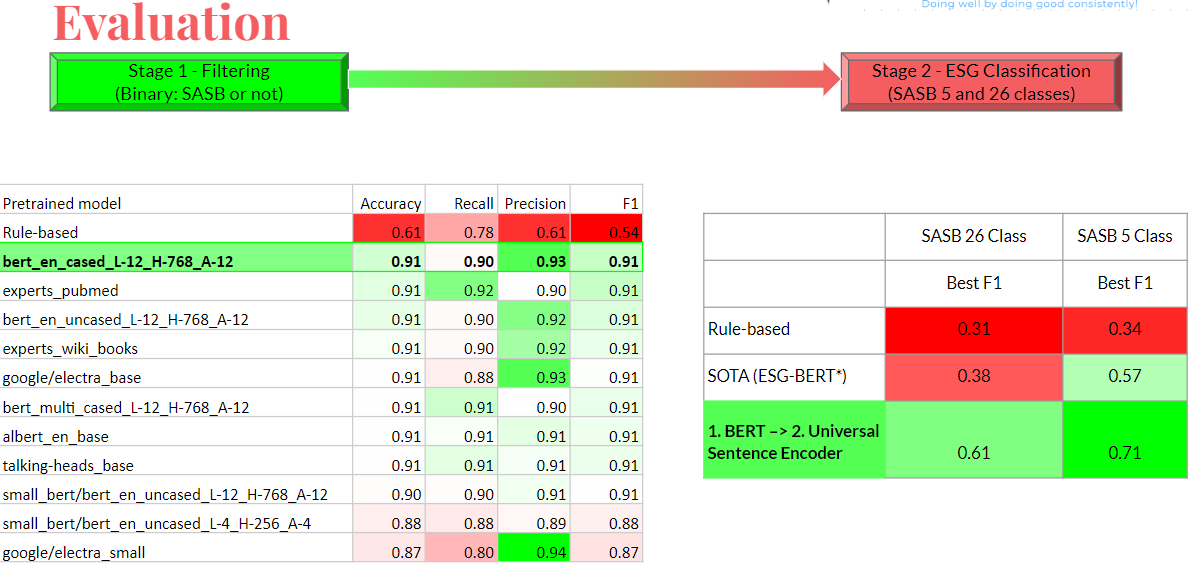
Please find more details in this document on our model specs and evaluations.